Index

This module translates DNA sequences into proteins, finds rare codons and helps design protein mutants conveniently.
DNA TO PROTEIN TRANSLATION
Pasting a DNA sequence will instantly produce 3 protein translation frames in the output.
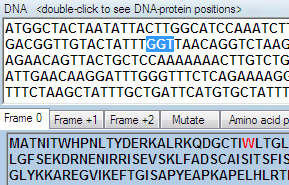
highlighted codon points out its amino acid in the protein sequence
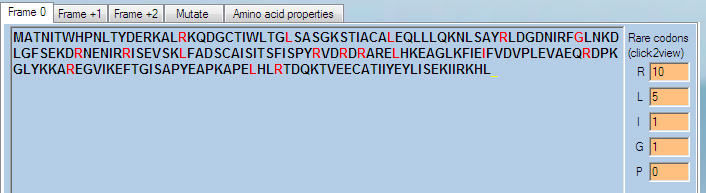
RARE CODONS
Rare codons can be the reason for poor expression of some proteins in E.Coli. Codon-compensated bacterial strains are recommended for expression of these proteins. Rare codons can be highlighted in DNA sequence by clicking the corresponding rare codon text fields, to the right of the protein sequences.
CLICK-MUTAGENESIS AND PCR PRIMER DESIGN
To find protein residues corresponding to DNA positions (and vice versa) double-click letters in DNA and protein sequences. Related residues will be highlighted in red in protein when a letter from DNA sequence is double-clicked and in red in DNA, when a letter from the protein sequence is double-clicked. The highlighted codons and amino acids can be mutated using the mutagenesis panel.
Highlighted codon can be changed to other codons in the Mutate window using the annotated drop-down codon list. The 5' and 3' flanking ends of the primer are adjusted to a desired melting temperature. For PCR, it is advised to adjust length of flanking sequences such that all values in the panel and the DNA sequence are optimal, i.e. highlighted green.
It is possible to design single primers with up to three mutations at once. Deletion or insertion mutagenesis primers can be designed similarly.
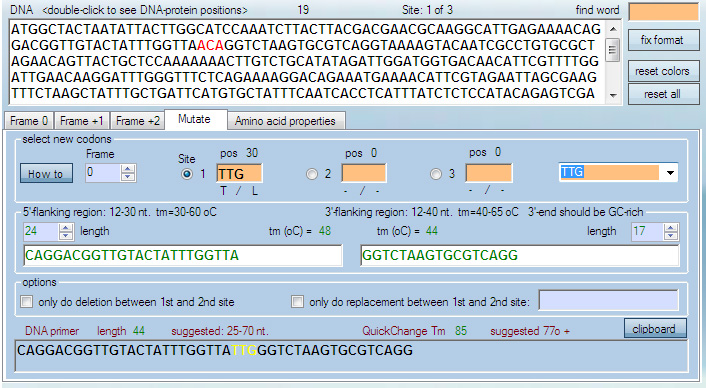
In all cases, PCR mutagenesis is performed with a single primer. Complementary primers are not designed because they are not used for the PCR reaction.
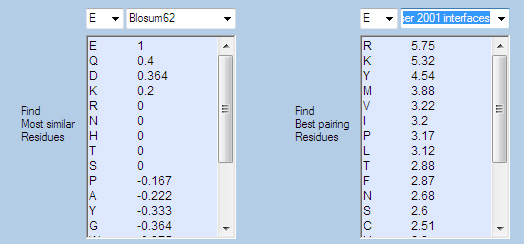
MUTAGENESIS ASSISTANT
This module quantitatively evaluates how similar an amino acid is to other amino acids. This utility is valuable for designing "most disruptive" or "most non-disruptive" mutations, for designing compensatory mutations or mutations that block some protein functions without perturibing the protein strongly.